4. Bootstraping and Causal Forest Analysis#
In this lab, we cover the application of bootstrapping and causal forest analysis within the context of econometric modeling and causal inference.
The bootstrapping section focuses on computing the standard errors of 1,000 bootstrap estimates for specific variables in a linear regression model using the penn_jae.dat dataset. We filter the data to include only relevant treatment and control groups, transform variables, and specify the regression model. This section details the process of data preparation, model fitting, and bootstrap resampling. The results, including the standard errors for the treatment and key demographic variables, are presented in a comprehensive table.
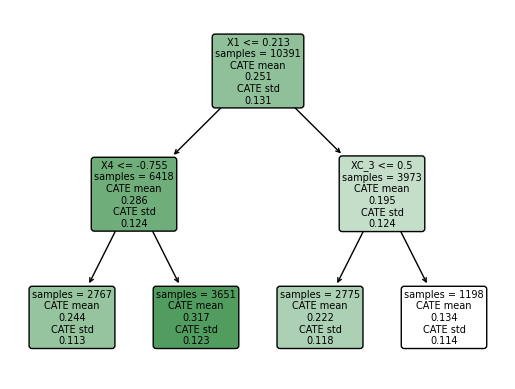
The causal forest analysis section replicates findings from the Athey and Wager (2018) paper. We follow structured steps to build the causal tree, estimate the Average Treatment Effect (ATE), and conduct a best linear predictor analysis. The analysis examines school-wise heterogeneity in treatment effects and compares results with and without clustering. Various plots are generated to visualize the heterogeneity of treatment effects across schools and the estimated Conditional Average Treatment Effect (CATE).
Through these exercises, students gain practical experience in implementing advanced econometric techniques in Python, R, and Julia, enhancing their understanding of causal inference and model validation in real-world data scenarios.